- Where and how does the agriculture drones market stand in the $40 billion overall market cap prediction for 2024?
- Ways Drones contribute to the Agriculture Development
- How farmers can take advantage of the Agriculture Drone’s Challenges
The use of drones in agriculture has been on the rise in the last couple of years. In fact, in the overall usage of tools and technology, drones are becoming a necessity in the modern world, especially in times of human isolation and physical distancing.
According to the European Commission’s Digital Transformation Мonitor, the overall market of the drone industry is expected to reach well over $21 billion in 2021, while the data from the WEF is predicting even higher rise of $40 billion in 2024.
With the rise of the IoT’s and the possibilities offered with it, the numbers for the future growth of the drone industry in agriculture are predicted to rise close to $5 billion, with the USA leading the market.
Ways Drones Contribute to the Agriculture Development
Drones are used in every step of the food growing process in the agriculture field. This includes soil and field analysis, planting, crop spraying, crop monitoring, irrigation, and health assessment.
Soil and field analysis
This step is the first one in the agricultural cycle. Drones are used for detailed crop analysis, as well as for precise 3D mapping. The design of seed patterns is remarkably cheaper compared to previous outdated methods.
Planting
The main benefit of using drones when planting is the reduction of the labor force. It drastically reduces the workforce needed for achieving the same goals. More exact numbers point to 85% reduction of planting costs. The way this works is by drones shooting plants and seeds directly into the soil.

Crop spraying
By scanning the ground with different types of lasers and cameras, the drones spray the exact amount of liquid needed and from the exact distance. Arguably, some estimates suggest an upwards of 500% efficiency in achieving this compared to standard machinery.

Crop monitoring
Large and vast fields of farmable land present the real problem here. Companies were using satellite images that showed significant flaws. These types of images were generated once a day, they were inaccurate and were pretty expensive. The use of drones allows for a far cheaper way of generating the images. Unlike with satellite monitoring, the weather doesn’t affect the image quality. The generation of multiple images per day is possible. Analysis suggests an increase of around 10% in crop yields.
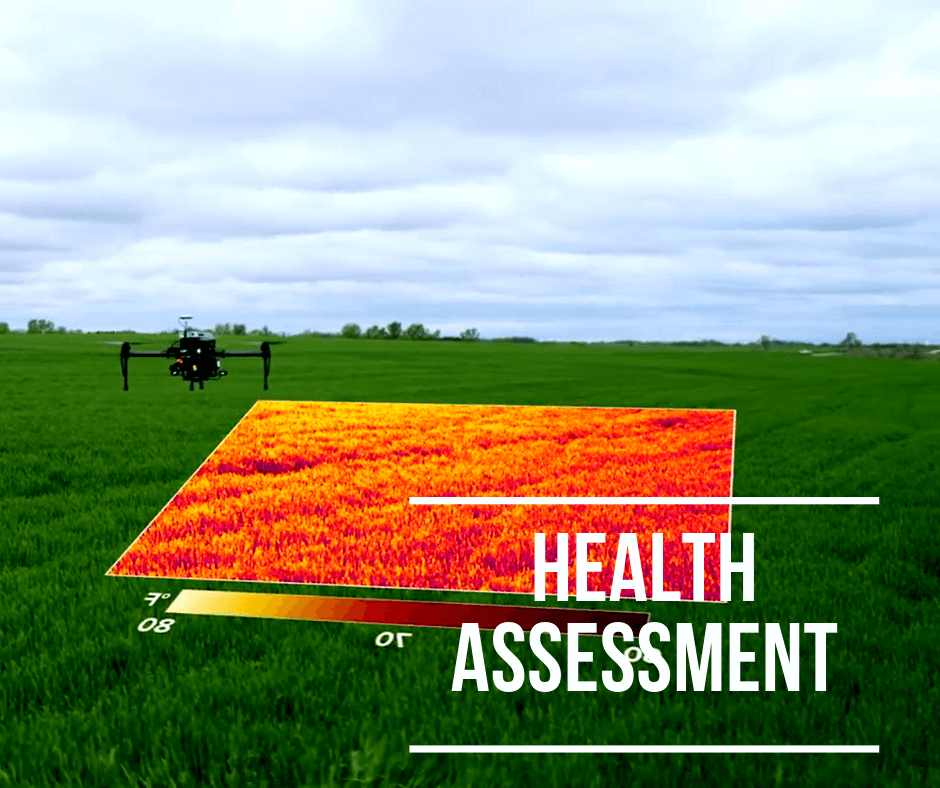
Health assessment
By using infrared cameras, drones are able to generate multispectral images of the crops, thus allowing for direct analysis of the health of the plants. This is extremely beneficial because it allows for early detection of bacterial and fungal infections. Early detection means an early response and an early response makes for an easier and quicker disease management action.
@droneacademyasia
Irrigation
Agriculture is by far the biggest consumer of usable water. Agriculture uses more than twice the amount of water used for industry. Too much water and irresponsible waste of our most precious resource can lead to serious problems in the long run. Drones equipped with thermal, hyperspectral, and multispectral sensors are able to detect areas that are too dry or too moist which allows for an appropriate response.
Farmers Need to Overcome the Agriculture Drone’s Challenges
Despite being an essential branch of our lives, agriculture still remains a low-margin business for most farmers. Farmers are still heavily reliant on their governments to provide help in tough times. More than 50% of the farmers in the US and Europe are over 55 years old. They often lack basic digital skills and are unlikely to change their habits. Less than 50% of them use computers and only around 40% use smartphones or tablets for business purposes. All of these factors heavily contribute to the lack of drones used in agriculture.
Companies have noticed this opportunity, and have begun to provide farmers with adequate help, services, and education. Individual drone pilots are also joining the game, by capturing the moment to offer their services too. Farmers like it or not will have to start adjusting and implementing the new technology in order to get the most out of their land. Likely more and more companies are entering the field, and more education, equipment, and funding are provided.
Damjan Mladenov, TheDronesWorld.net
Humans are creatures of habits, and old habits die hard. But it’s only when we break free of those habits that we really start to grow.

